- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
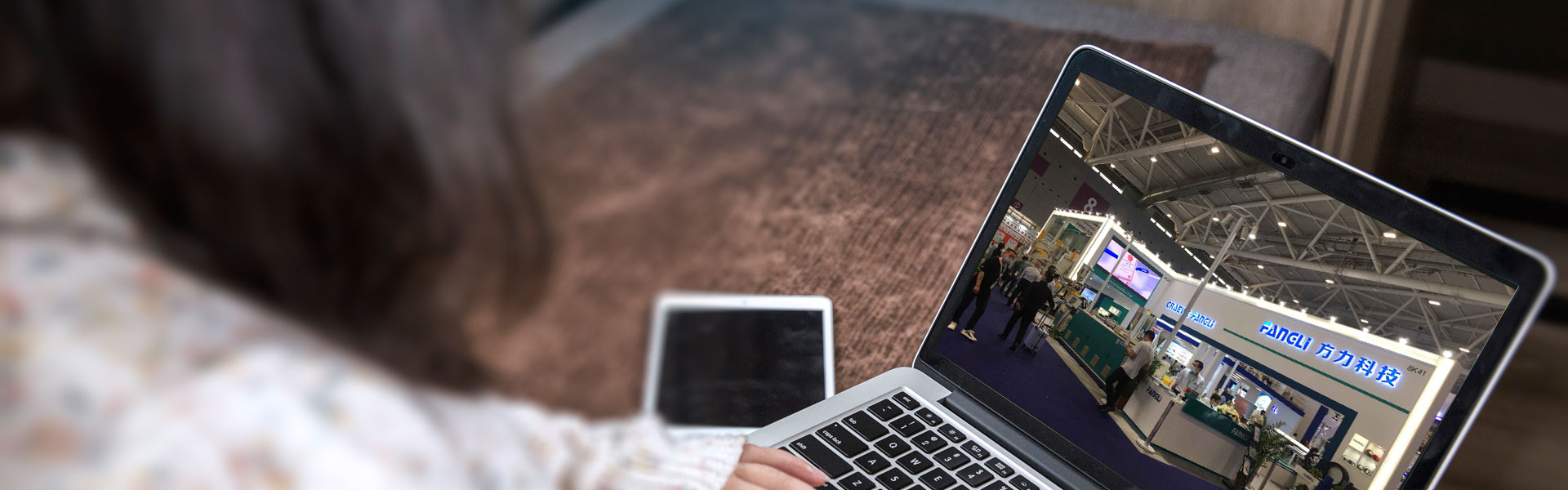
How to make Fancy Extrusion Line for Special Application Pipe
2024-05-23
Creating a fancy extrusion line for special application pipes involves several steps and considerations, including equipment selection, material handling, process optimization, and quality control. Here's a detailed guide to help you design and implement an efficient extrusion line:
1. Define the Application and Specifications
· Identify the Application: Determine the specific application for the pipes, such as medical tubing, automotive parts, or industrial hoses.
· Material Selection: Choose the appropriate material (e.g., PVC, PE, PP, PTFE) based on the application requirements.
· Pipe Specifications: Define the pipe dimensions, tolerances, mechanical properties, and any special features like multilayer structures or embedded components.
2. Equipment Selection
· Extruder: Choose an extruder with the right screw design and length-to-diameter (L/D) ratio for the material and output required. For special applications, consider a twin-screw extruder for better mixing and homogeneity.
· Die and Tooling: Select a die that matches the pipe’s cross-sectional shape and size. Consider using adjustable dies for more flexibility.
· Cooling System: Implement an effective cooling system (water bath, air cooling, or a combination) to solidify the extruded pipe uniformly.
· Haul-Off Unit: Ensure the haul-off unit has the appropriate number of belts or caterpillars to pull the pipe consistently without deformation.
· Cutting and Handling Equipment: Choose between a rotary cutter, fly-knife cutter, or planetary cutter depending on the pipe’s size and material.
3. Material Handling
· Feeding System: Use gravimetric feeders for precise material dosing. For specialty materials, consider using a compounding system to blend additives or colorants uniformly.
· Drying System: Some polymers require drying before extrusion to remove moisture that could cause defects. Use a dehumidifying dryer for this purpose.
4. Process Optimization
· Temperature Control: Maintain precise control over the barrel and die temperatures to ensure consistent material flow and quality.
· Screw Speed and Pressure: Optimize the screw speed and extrusion pressure to achieve the desired output rate while maintaining quality.
· Cooling Rate: Adjust the cooling rate to avoid warping or stress in the pipes. This is critical for pipes with tight dimensional tolerances.
5. Quality Control and Monitoring
· Inline Measurement: Implement inline measurement systems (ultrasonic or laser gauges) to monitor pipe dimensions and detect defects in real-time.
· Automated Control Systems: Use PLCs or SCADA systems to automate process control and ensure consistency.
· Quality Assurance: Conduct regular physical and mechanical tests (e.g., tensile, compression, and impact tests) to verify that the pipes meet the specified requirements.
6. Additional Features for Special Applications
· Co-extrusion: For pipes requiring multiple layers, use a co-extrusion setup with multiple extruders feeding into a common die.
· Reinforcement: For reinforced pipes, incorporate braiding or winding equipment to add strength.
· Surface Treatment: Consider surface treatments such as corona or plasma treatment for better adhesion of coatings or to modify surface properties.
7. Safety and Compliance
· Safety Measures: Implement safety guards, emergency stop buttons, and interlocks to protect operators.
· Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the extrusion line complies with relevant industry standards and regulations, such as FDA, ISO, or specific industry certifications.
Example Layout of a Fancy Extrusion Line
1. Material Preparation:
· Material handling and drying systems.
2. Extruder:
· Main extruder (single or twin-screw) with precise temperature control.
3. Co-Extruder (if needed):
· For multilayer pipes.
4. Die Head:
· Custom-designed die for special pipe shapes or structures.
5. Calibration and Cooling:
· Vacuum calibration table and cooling tanks.
6. Haul-Off Unit:
· Multiple caterpillar belts for uniform pulling.
7. Cutting and End-Forming:
· Automatic cutting unit and end-forming stations (e.g., for flaring or threading).
8. Inline Quality Control:
· Laser or ultrasonic measuring devices.
9. Winding or Stacking:
· For flexible pipes, an automatic winding machine; for rigid pipes, a stacking system.
Conclusion
Designing a fancy extrusion line for special application pipes requires careful planning and attention to detail. By selecting the right equipment, optimizing the process, and implementing rigorous quality control, you can produce high-quality pipes that meet specific application needs. Regular maintenance and continuous process improvement will ensure long-term success and efficiency.