- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
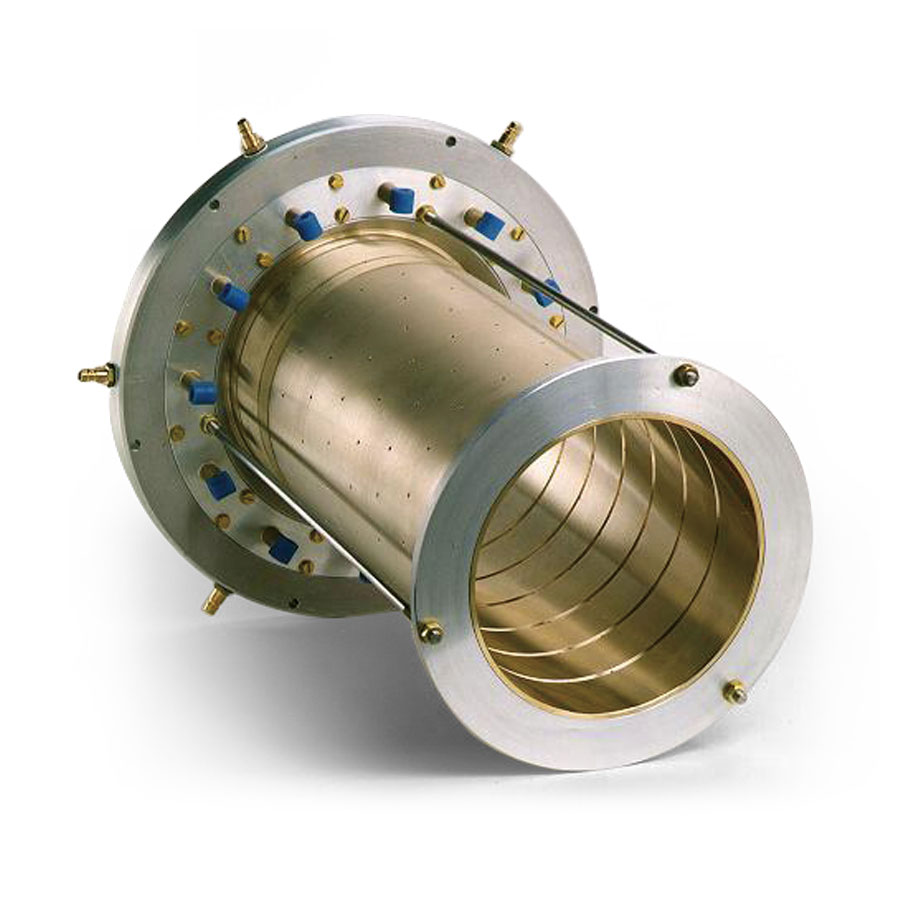
What is a Customized Calibration Sleeve?
2025-04-03
It’s a precision-engineered sleeve or pipe section made to mimic:
Pipeline internal diameter (ID)
Wall thickness
Ovality, dents, weld seams, or other features
Specific defect profiles (for ILI tools)
Used for:
Calibrating pig passage
Validating sizing and gauging tools
Training smart pigging or inline inspection (ILI) tools
✅ How to Effectively Use a Customized Calibration Sleeve
1. Design for Application
Customize based on:
Pipeline diameter and material
Known anomalies (e.g., dents, weld beads, ovality)
Tool specs (mandrel pigs, caliper pigs, EMAT, MFL tools, etc.)
Work with the tool vendor to ensure compatibility with inspection equipment.
2. Pre-Calibration Prep
Ensure the sleeve is:
Clean, rust-free, and dry
Stored in a controlled environment
Measure and verify tolerances (often within ±0.1 mm)
3. Tool Insertion
Mount the sleeve on a horizontal test bed or frame
Carefully insert the pig or inspection tool
Use lubricants if needed (especially with metal-on-metal contact)
4. Run Calibration
Pass the tool through at controlled speed or pressure
Confirm:
Smooth passage
Sensor or caliper readings match sleeve dimensions
Proper detection of defects or internal features (for smart tools)
5. Record Data
Compare tool data to known calibration sleeve profile
Analyze results for tool accuracy and sensitivity
Document all calibration runs for compliance and QA
6. Post-Use Cleaning and Storage
Clean the sleeve (especially around simulated welds or defects)
Store in a dry, padded rack to prevent mechanical damage
Inspect regularly for wear or deformation
Benefits of Customization:
Matches real-world pipe conditions
Improves accuracy and repeatability
Helps qualify tools before expensive field runs